
2024.9---2027.6 Master's Student
My research interests lie at the intersection of astronomy and artificial intelligence, focusing on multimodal perception, large language models, space mission instruction parsing, and autonomous reasoning for space applications. I conduct astronomical research under the supervision of Prof. Nan Li at the National Astronomical Observatories (NAOC) and Prof. Ning An at the Changchun Observatory, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
I am currently a research intern at The Future Laboratory, Tsinghua University, where I am working on developing large-scale lunar language models and intelligent systems for lunar exploration. Previously, I interned at the National Astronomical Observatories, CAS and the Department of Earth and Space Sciences, SUSTech, gaining hands-on experience in cutting-edge astronomical and space science projects.
Warning
Problem: The current name of your GitHub Pages repository ("Solution: Please consider renaming the repository to "
http://".
However, if the current repository name is intended, you can ignore this message by removing "{% include widgets/debug_repo_name.html %}" in index.html.
Action required
Problem: The current root path of this site is "baseurl ("_config.yml.
Solution: Please set the
baseurl in _config.yml to "Education
-
 University of Chinese Academy of SciencesMaster's Student, School of Astronomy and Space ScienceSep. 2024 - present
University of Chinese Academy of SciencesMaster's Student, School of Astronomy and Space ScienceSep. 2024 - present -
 Qilu University of Technology (Shandong Academy of Sciences)B.S. in Computer ScienceSep. 2020 - Jun. 2024
Qilu University of Technology (Shandong Academy of Sciences)B.S. in Computer ScienceSep. 2020 - Jun. 2024
Honors & Awards
-
Graduate Academic Scholarship, UCAS2024 - present
-
Quancheng Scholarship2024
-
National Scholarship, Ministry of Education2023
-
National Encouragement Scholarship2022
News
Selected Publications (view all )
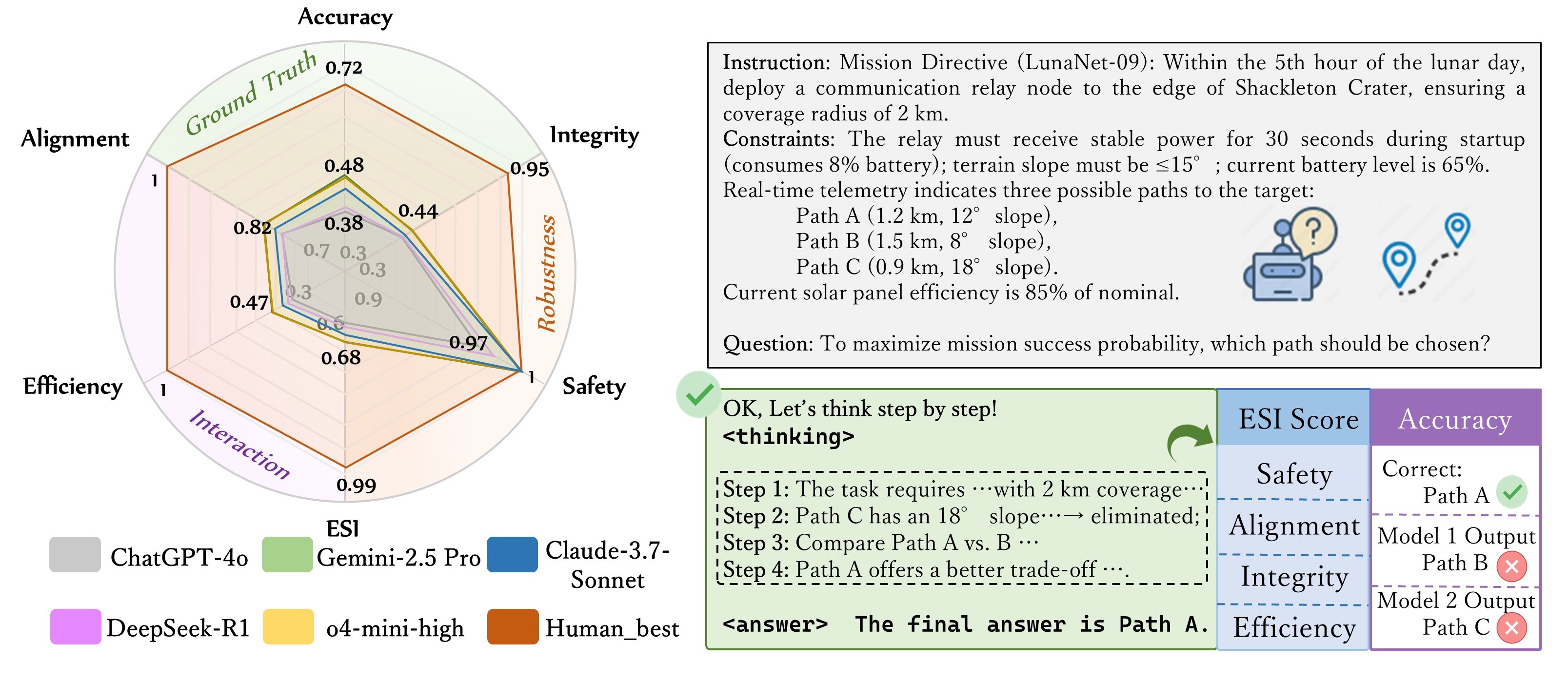
Lunar-Bench: Evaluating Task-Oriented Reasoning of LLMs in Lunar Exploration Scenarios
Xin-Yu Xiao, Ye Tian, Yalei Liu, Xiangyu Liu, Tianyang Lu, Erwei Yin, Qianchen Xia, Shanguang Chen
Submitted to NeurIPS 2025 Under Review
This paper introduces Lunar-Bench, the first benchmark designed to rigorously evaluate the reasoning and decision-making capabilities of large language models (LLMs) under the unique constraints of lunar exploration. Featuring 3,000 high-fidelity tasks across critical lunar operational domains, Lunar-Bench goes beyond accuracy metrics by proposing Environmental Scenario Indicators (ESI), which assess models' safety, efficiency, factual integrity, and alignment. Evaluations of 36 state-of-the-art LLMs reveal significant performance gaps compared to human experts, underscoring the urgent need for robust, domain-adapted solutions in mission-critical AI deployment.
Lunar-Bench: Evaluating Task-Oriented Reasoning of LLMs in Lunar Exploration Scenarios
Xin-Yu Xiao, Ye Tian, Yalei Liu, Xiangyu Liu, Tianyang Lu, Erwei Yin, Qianchen Xia, Shanguang Chen
Submitted to NeurIPS 2025 Under Review
This paper introduces Lunar-Bench, the first benchmark designed to rigorously evaluate the reasoning and decision-making capabilities of large language models (LLMs) under the unique constraints of lunar exploration. Featuring 3,000 high-fidelity tasks across critical lunar operational domains, Lunar-Bench goes beyond accuracy metrics by proposing Environmental Scenario Indicators (ESI), which assess models' safety, efficiency, factual integrity, and alignment. Evaluations of 36 state-of-the-art LLMs reveal significant performance gaps compared to human experts, underscoring the urgent need for robust, domain-adapted solutions in mission-critical AI deployment.
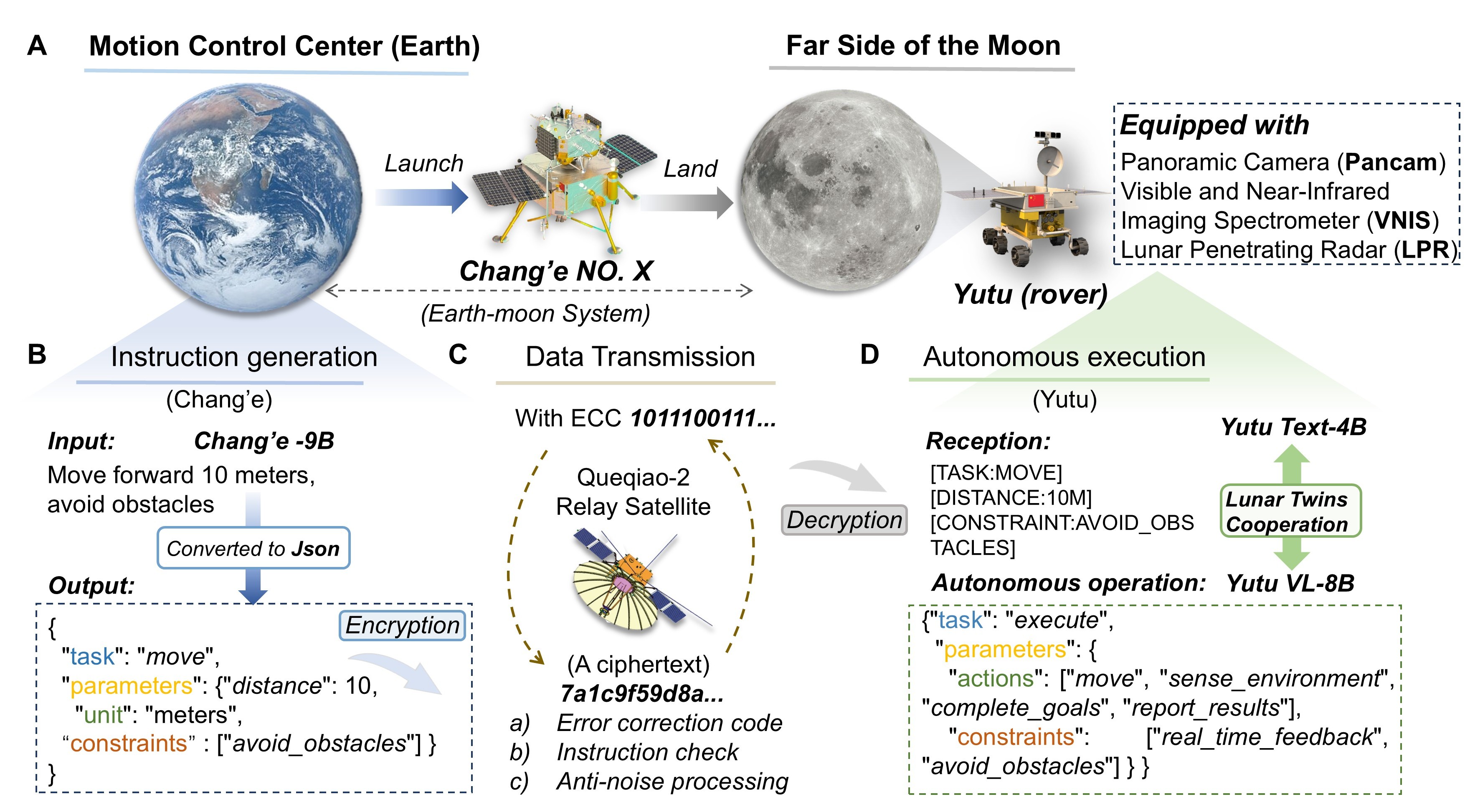
Lunar Twins: We Choose to Go to the Moon with Large Language Models
Xin-Yu Xiao, Yalei Liu, Xiangyu Liu, Zengrui Li, Erwei Yin, Qianchen Xia
Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL) 2025 Accepted
This paper presents Lunar Twins, the first large language models specifically designed for lunar exploration. The system includes the Chang’e and Yutu models, introduces a collaborative multi-agent workflow (Lunar_GenData), and establishes the first specialized lunar dataset integrating data from the Chang’e missions. Extensive experiments show that Lunar Twins significantly outperform comparable models in domain expertise and hint at embodied intelligence potential.
Lunar Twins: We Choose to Go to the Moon with Large Language Models
Xin-Yu Xiao, Yalei Liu, Xiangyu Liu, Zengrui Li, Erwei Yin, Qianchen Xia
Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL) 2025 Accepted
This paper presents Lunar Twins, the first large language models specifically designed for lunar exploration. The system includes the Chang’e and Yutu models, introduces a collaborative multi-agent workflow (Lunar_GenData), and establishes the first specialized lunar dataset integrating data from the Chang’e missions. Extensive experiments show that Lunar Twins significantly outperform comparable models in domain expertise and hint at embodied intelligence potential.
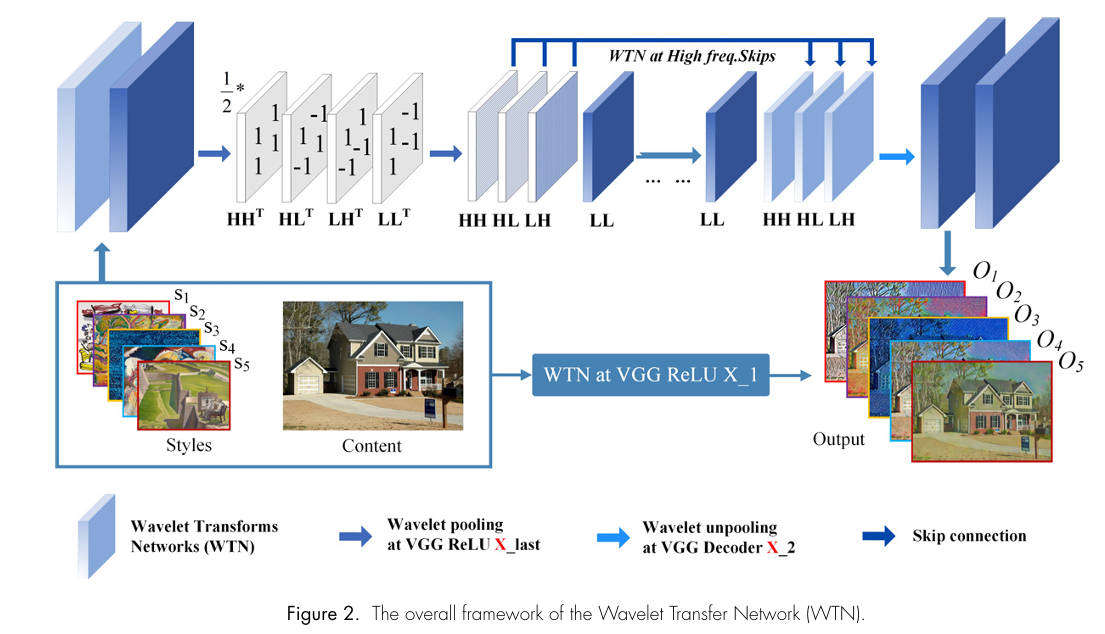
Integrating Wavelet Transforms into Image Reconstruction Networks for Effective Style Transfer
Yunfei Chu, Xin-Yu Xiao, Longchen Han, Yaoshun Yue, Maohai Lin
Journal of Imaging Science and Technology 2025 Published
This paper presents an effective method for image style transfer by integrating wavelet transforms into whitening and coloring processes within image reconstruction networks. The proposed Wavelet Transfer Network (WTN) directly aligns the feature covariance of content and style images, yielding high-quality stylized outputs with enhanced efficiency and generalization. Experimental results demonstrate the superiority of WTN over existing methods in both arbitrary and photorealistic style transfer, setting a new benchmark in the field.
Integrating Wavelet Transforms into Image Reconstruction Networks for Effective Style Transfer
Yunfei Chu, Xin-Yu Xiao, Longchen Han, Yaoshun Yue, Maohai Lin
Journal of Imaging Science and Technology 2025 Published
This paper presents an effective method for image style transfer by integrating wavelet transforms into whitening and coloring processes within image reconstruction networks. The proposed Wavelet Transfer Network (WTN) directly aligns the feature covariance of content and style images, yielding high-quality stylized outputs with enhanced efficiency and generalization. Experimental results demonstrate the superiority of WTN over existing methods in both arbitrary and photorealistic style transfer, setting a new benchmark in the field.